Meet butyrate—a short-chain fatty acid that plays a vital role in gut health. Despite being lesser known than probiotics or fibre, butyrate is essential for maintaining a thriving gut microbiome and supporting overall wellness. It is one of the primary energy sources for colon cells and plays a vital role in maintaining gut health. In this article, we’ll explore what butyrate is, its benefits, and how to naturally increase its production for optimal gut health.
🧠 Prefer to watch instead of read?
Scroll to the end for our quick explainer 4 minutes video on Butyrate and it’s health Benefits.
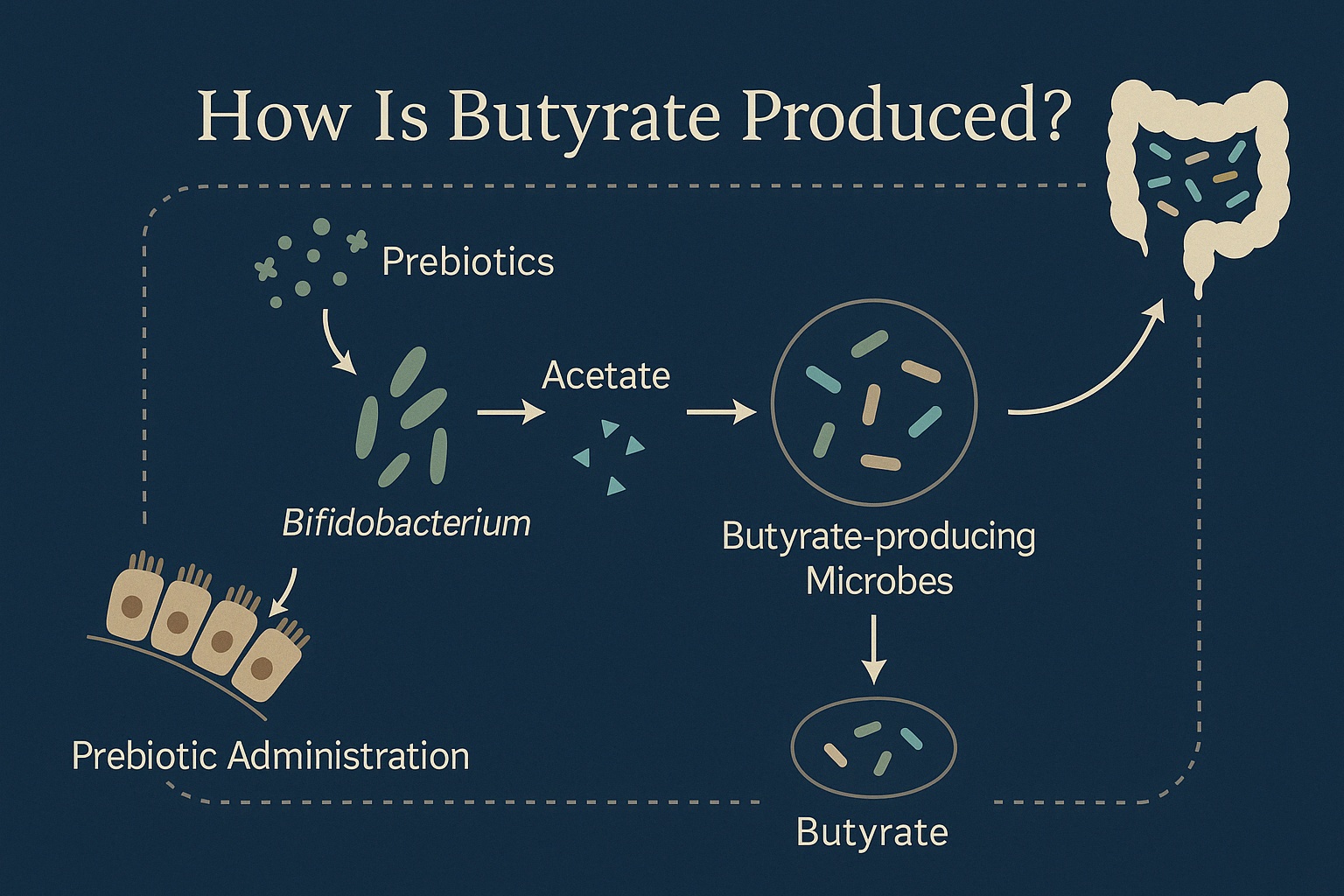
How is Butyrate Produced?
The process begins when we consume foods rich in dietary fibres, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These fibres travel to the large intestine, where they are broken down by beneficial bacteria. During this fermentation process, butyrate is produced alongside other SCFAs like acetate and propionate.
The Benefits of Butyrate for Gut Health
Butyrate offers several benefits that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Let’s delve into some of the most important ones.
Supports Colon Health
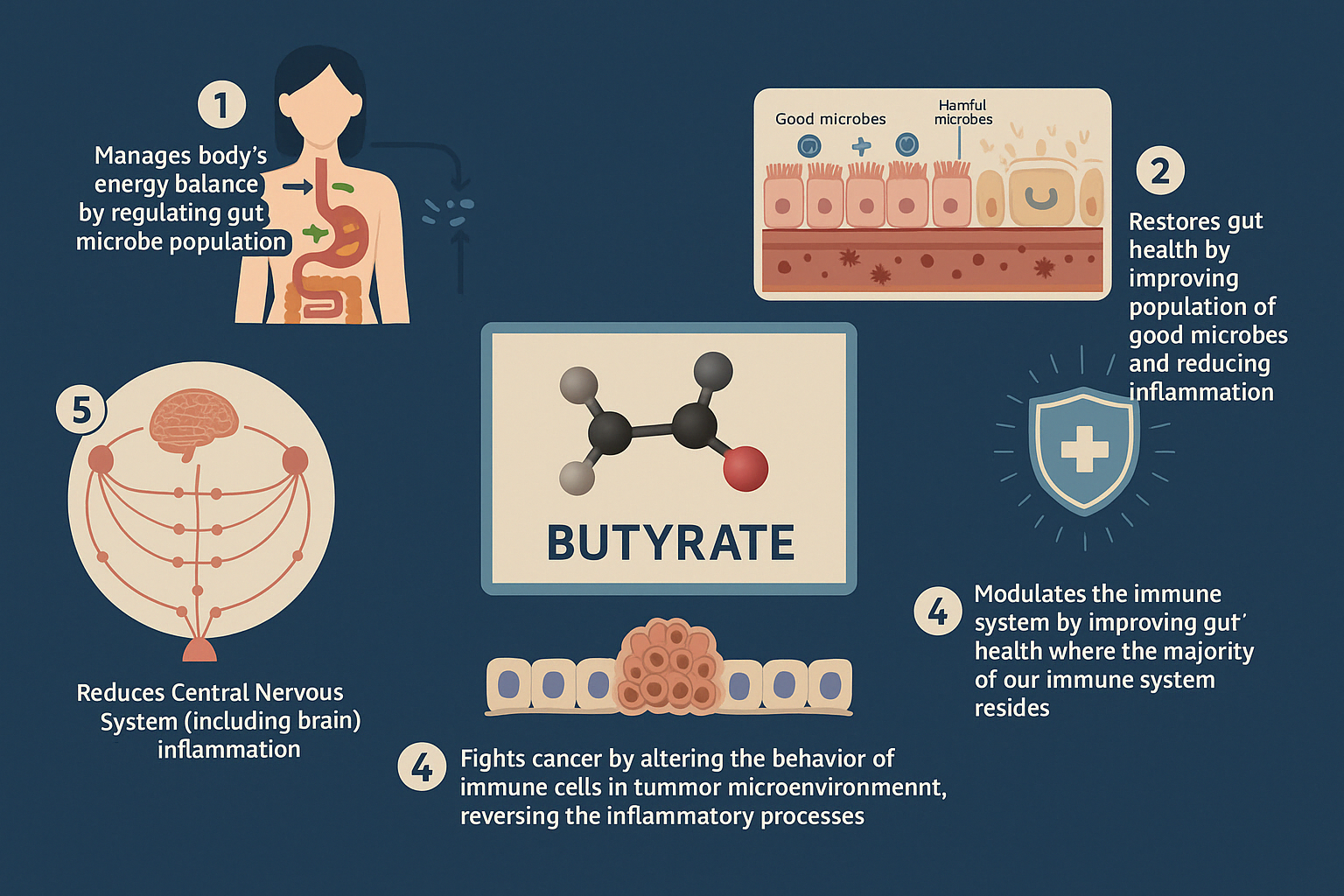
Butyrate is the primary energy source for the cells lining the colon, known as colonocytes. Research indicates that Butyrate helps strengthen the wall of your intestines, which is essential to keeping bad stuff in your gut from leaking into your body. It does this by helping cells make a strong, sticky mucus that coats the intestine and by reinforcing the connections between cells, like adding extra locks to a gate. Butyrate also helps your immune system by balancing the good and bad immune cells in your gut, which keeps things calm and prevents your body from attacking itself.
Reduces Inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can lead to a variety of health issues, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Studies have shown butyrate helps reduce inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) by inhibiting NF-κB, a key protein that activates genes causing inflammation. By blocking NF-κB, butyrate lowers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, and promotes a healthier gut environment.
Promotes a Balanced Gut Microbiome
A diverse and balanced gut microbiome is crucial for optimal health. Butyrate-producing bacteria help maintain this balance by supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful ones. This balance contributes to improved digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. Research indicates that butyrate plays a role in regulating immune function and maintaining intestinal homeostasis.
May Prevent Colon Cancer
Research suggests that butyrate has potential anti-cancer properties. It may help prevent the development and progression of colon cancer by promoting healthy cell growth and inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancerous cells. Butyrate can also change how DNA is organized, helping to shut down cancer cells and prevent their growth.

How to Increase Butyrate Production?
To reap the benefits of butyrate, it’s essential to support its production in the gut. Here are some ways to increase butyrate production naturally:
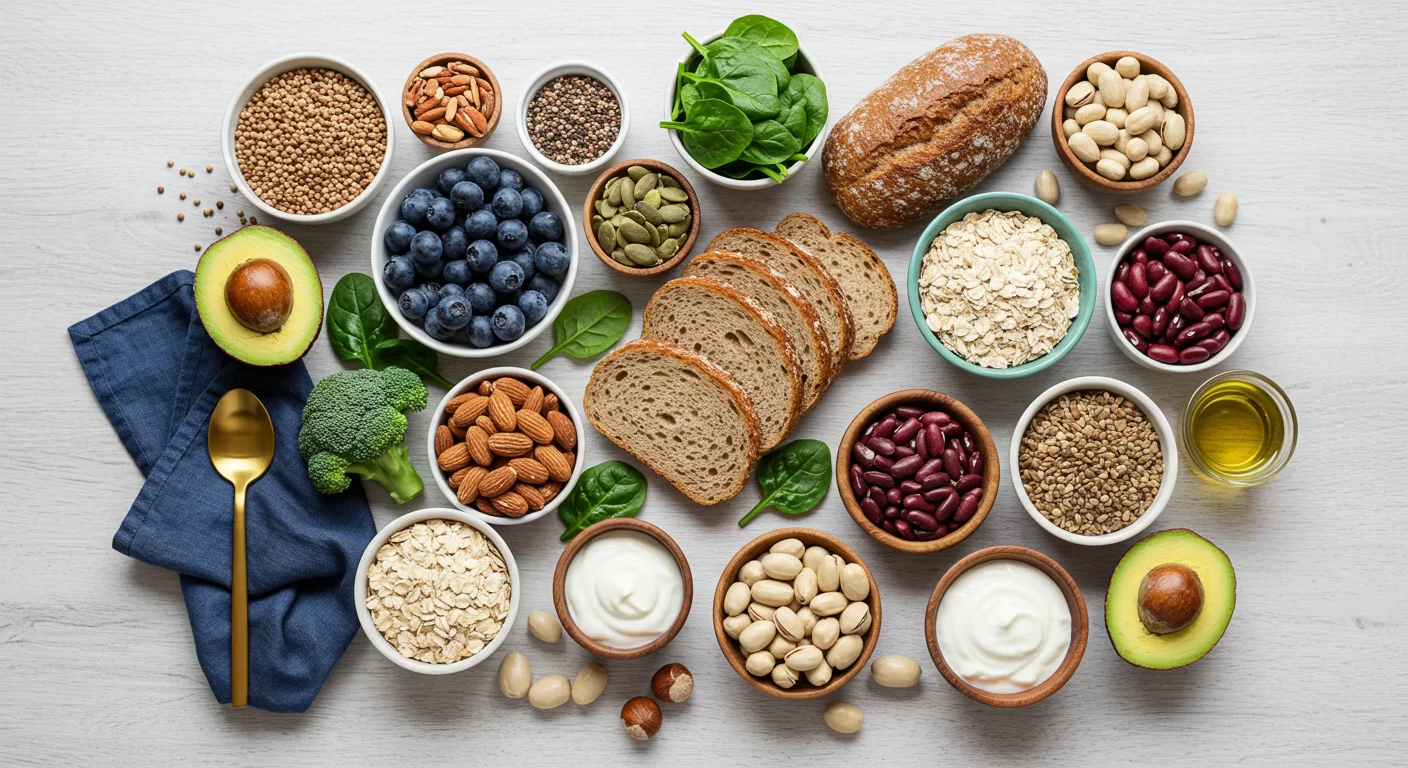
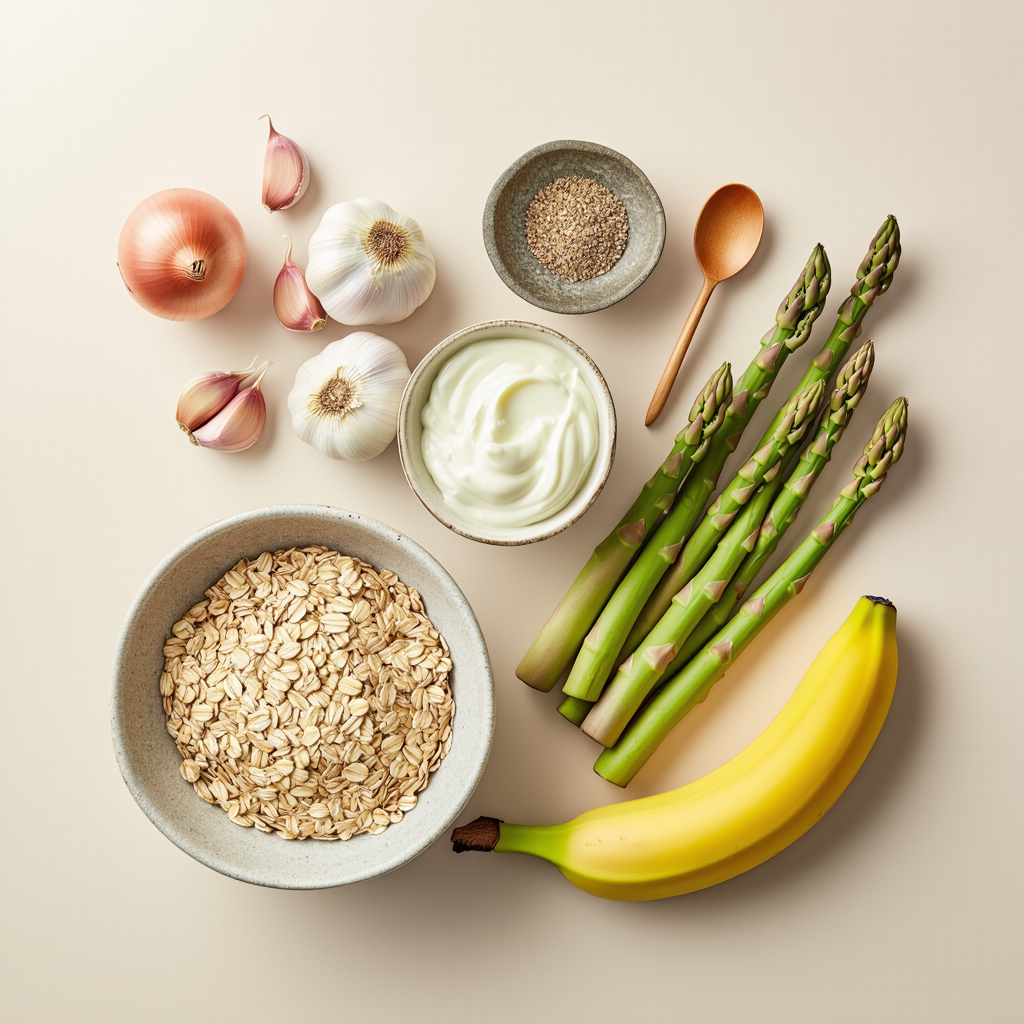
Consume a Fiber-Rich Diet
A diet rich in dietary fibers is key to promoting butyrate production. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts in your meals. Foods like oats, bananas, and asparagus are particularly beneficial for boosting butyrate levels.
Incorporate Prebiotics and Probiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria, while probiotics are live bacteria that contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. Combining both in your diet can enhance butyrate production. Prebiotic-rich foods include garlic, onions, and leeks, while probiotic sources include yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables.
Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining a healthy gut environment. Water helps keep the digestive system functioning smoothly, supporting the fermentation process that produces butyrate.
Limit Processed Foods and Sugars
Processed foods and added sugars can negatively impact gut health by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria. Limiting their intake can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome and support butyrate production.
Sodium Butyrate Supplements
While dietary sources of butyrate—such as oats, bananas, and asparagus—help nourish gut bacteria, sodium butyrate, or tributyrin supplements provide a more concentrated boost. Tributyrin has higher bioviability and provides slow release. Both supplements can supports gut lining integrity, reduces inflammation, and enhances microbiome balance. It can be particularly beneficial for individuals struggling to produce sufficient butyrate naturally.
The Connection Between Butyrate and Overall Health.
Butyrate’s benefits extend beyond gut health, impacting various aspects of overall well-being. Here are a few ways butyrate contributes to general health:
Supports Mental Health
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network between the gut and the brain. As a product of gut bacteria, butyrate can directly affect the brain by crossing the blood-brain barrier or indirectly by stimulating nerves like the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is like a superhighway that connects your brain to your gut and other organs, carrying messages back and forth. This microbial metabolite can modulate the production and activity of key neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, GABA, dopamine, and serotonin, which play crucial roles in mood, cognition, and behavior. By influencing them and their neural pathways, butyrate helps maintain balance and communication along the gut-brain axis, promoting overall well-being. You can learn more about the gut-brain connections in our dedicated article.
Regulates Metabolism
Butyrate has been shown to regulate metabolism by enhancing energy expenditure and reducing fat storage. This can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Research indicates that butyrate improves insulin sensitivity and increases energy expenditure.
Strengthens Immune Function
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for a robust immune system. Butyrate supports immune function by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing inflammation, helping to protect against infections and diseases. Butyrate has been found to regulate immune responses and maintain intestinal homeostasis.
Enhances Cardiovascular Health
Research suggests that butyrate may improve cardiovascular health through several actions like reducing inflammation and improving how the body handles fats and sugars. Butyrate helps in managing cholesterol levels, reducing obesity, and improving how the body uses insulin. Its actions aren’t limited to the gut, and it also impacts other organs and systems to protect the heart and blood vessels. Studies also show butyrate can improve heart tissue damage and protect heart tissue architecture.

Why Butyrate Deserves a Place in Your Gut Health Routine
Butyrate is a key short-chain fatty acid that supports gut health, reduces inflammation, and promotes a balanced microbiome. It may also help protect against colon cancer.
To naturally boost butyrate, prioritise a fibre-rich diet, prebiotics and probiotics, hydration, and limiting processed foods. These habits enhance gut function and overall well-being.
By understanding butyrate’s role, you can take meaningful steps towards better health. Embrace its benefits and nurture your gut for a healthier, more vibrant life.
Join Us in Redefining Beauty
Subscribe for Exclusive Insights










