Collagen supplements are everywhere, promising smoother skin, fewer wrinkles, and a youthful glow. But amidst the buzz, a healthy dose of skepticism is understandable. Do these popular powders and drinks really deliver on their claims, or is it just clever marketing? If you’re seeking genuine, science-backed answers, you’re in the right place. If you’ve looked at collagen before and after photos and wondered if they’re real, this article is for you.
This article provides a balanced, evidence-based look at whether oral collagen supplements – specifically the commonly studied hydrolyzed collagen peptides – genuinely offer benefits for different health areas, with a particular focus on skin health.
We’ll delve into the science, examine findings from clinical studies, openly discuss the limitations, and address questions like how long for collagen to work. Our commitment is to empower you with transparent and trustworthy information.
How Are Collagen Supplements Supposed to Work? (The Science Explained)
To understand if collagen supplements work, we first need to look at how they’re designed to interact with our bodies.
From Protein to Peptides: The Role of Hydrolysis
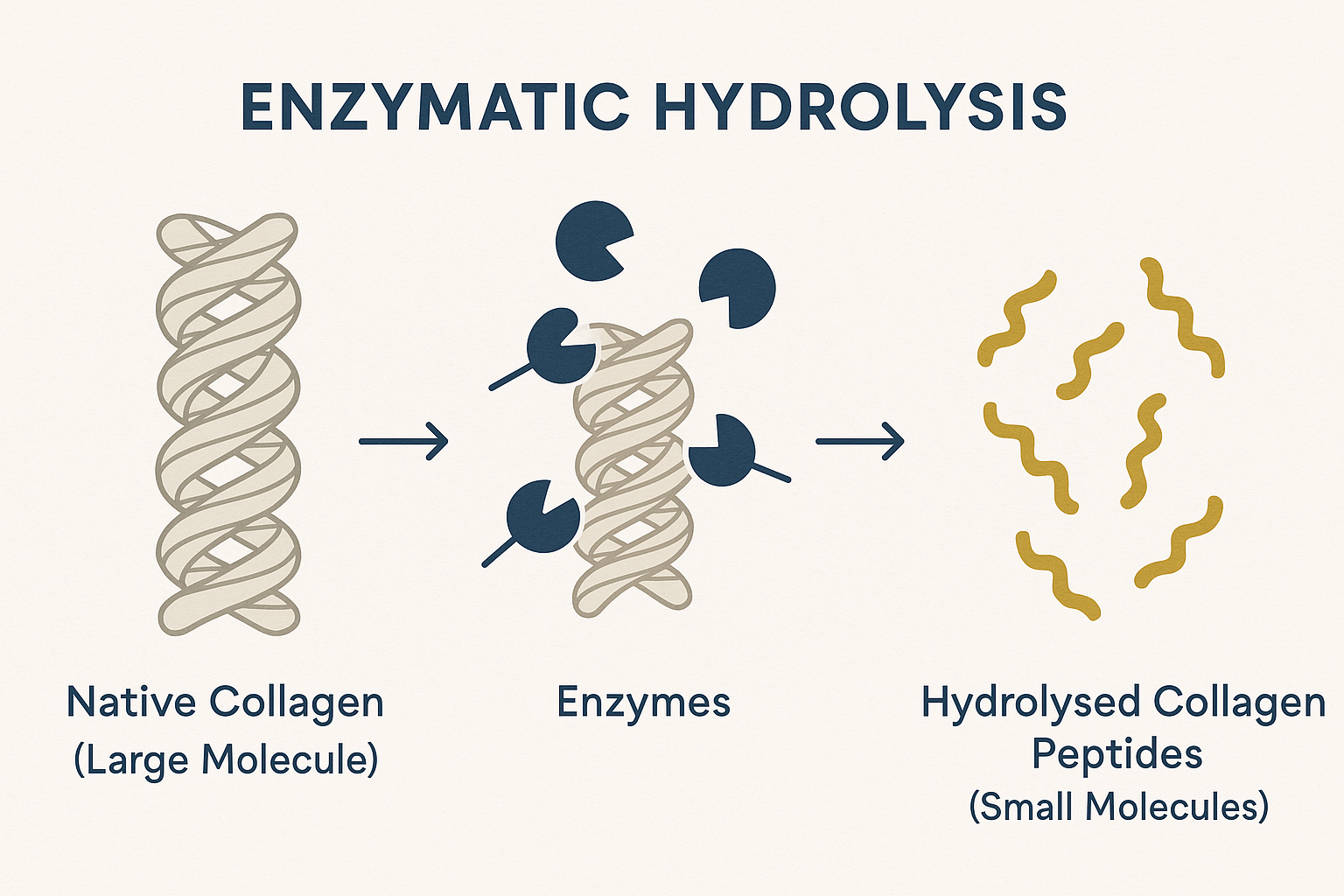
Native collagen, found naturally in animal tissues (like bovine collagen / beef collagen or marine collagen), is a very large protein molecule (around 300 kDa, think of kDa as a unit measuring the size or weight of these tiny protein pieces; a high kDa means a large molecule, and a low kDa means a small one.). While beneficial when consumed in foods like bone broth (providing amino acids), its sheer size limits its direct absorption.
High-quality supplements use enzymatic hydrolysis – a controlled process using specific enzymes to break down the large collagen protein into much smaller chains called collagen peptides (CP), also known as hydrolyzed collagen (HC), Hydrolysed Collagen Sources and Applications. These peptides typically have a low molecular weight (often below 5kDa, with many products aiming for <3kDa), which is key to their potential effectiveness.
This process gives us products like hydrolysed collagen peptides.
Absorption & Bioavailability: Getting Peptides into Your System
Why are smaller peptides better?
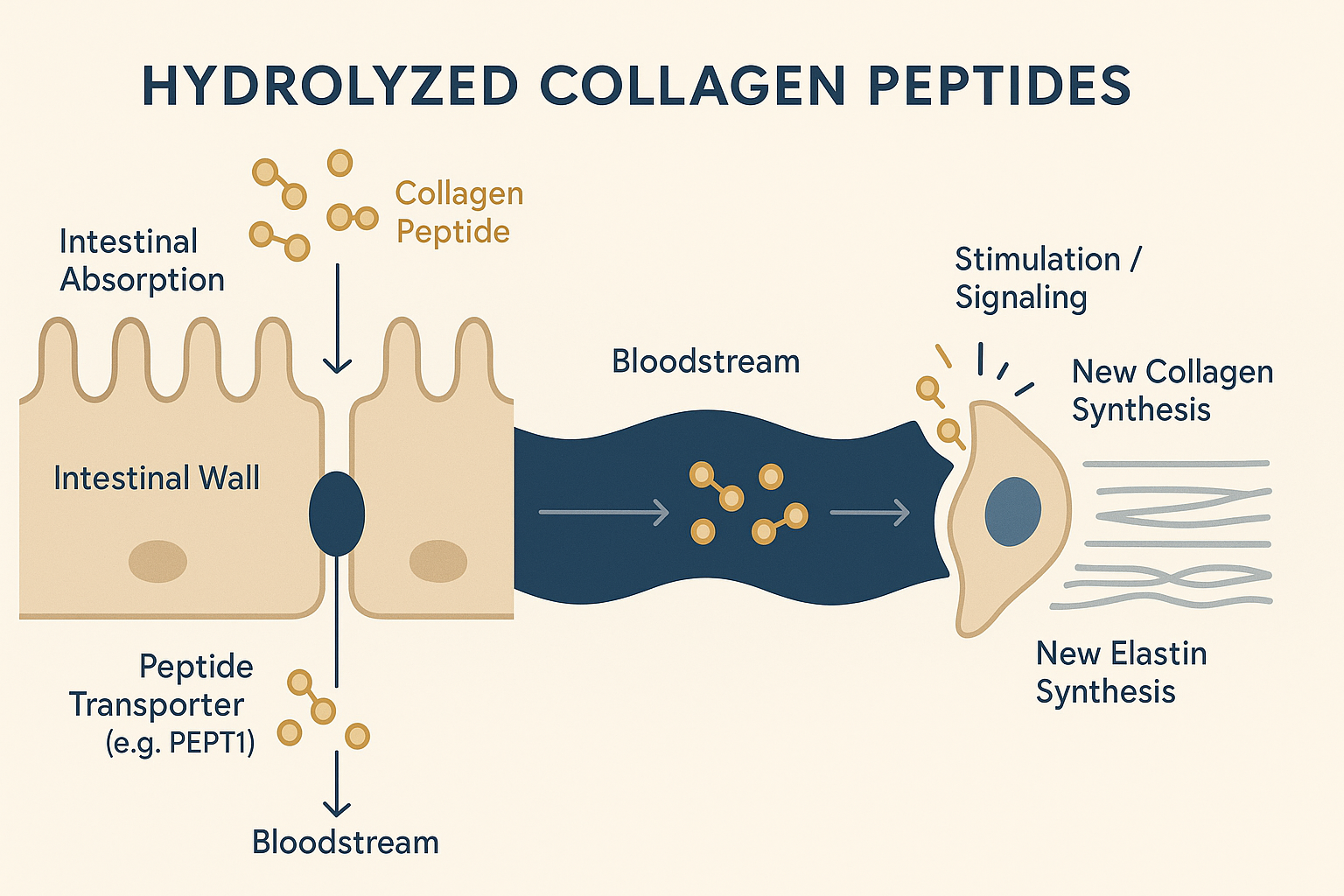
Because they can be more easily absorbed by your body. Unlike the large native collagen molecule, which is mostly broken down into individual amino acids during digestion, studies show that specific small collagen peptides (especially di- and tri-peptides containing the key amino acid hydroxyproline, like Pro-Hyp) can be absorbed partially intact through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream. They use specialized ‘doorways’ in the gut lining, known as peptide transporters, like PEPT1, which allow these short chains to pass through more readily than large proteins. Think of it like having a special VIP entrance just for these specific small peptides, allowing them to reach the bloodstream effectively.
Why is this effective absorption relevant?
Because many of these small peptides are considered ‘bioactive’. This means that beyond simply providing protein building blocks, they can have specific biological effects, such as sending signals to cells to boost the production of substances like collagen. Think of them as having a dual effect – providing raw materials and acting as crucial messengers.
Signaling Fibroblasts (and other cells): The Proposed Mechanism of Action
Once absorbed, these bioactive peptides circulate throughout the body and reach target tissues like the skin, joints, and bones.
The key hypothesis behind collagen supplementation is that these peptides don’t just act as building blocks; they function as signaling molecules. They essentially mimic the body’s own collagen breakdown products, sending a message to specialized cells like fibroblasts (in the skin), chondrocytes (in cartilage), and potentially osteoblasts (in bone).
This signal prompts these cells to ramp up their natural production of new collagen, as well as other crucial components of the tissue matrix, like elastin and hyaluronic acid, The Role of bioactive peptides in activating fibroblast.
In vitro studies support this, showing collagen peptides can increase collagen and elastin production by fibroblasts while reducing the activity of collagen-degrading enzymes (MMPs). If you’re wondering what are MMPs, they are enzymes that can break down collagen. Research exploring do MMPs damage collagen suggests that inhibiting these enzymes is part of how supplements might help preserve the skin matrix, The role of collagen derived bioactive peptides in regulating MMPs her.
What Does the Clinical Evidence Show? (Skin, Joints & More)
The theory of peptide signaling is compelling, but what do human clinical trials show? To assess this fairly, we look at the highest quality evidence available. When evaluating claims about collagen before and after results, it’s crucial to look at clinical trial data
Understanding the Evidence: RCTs and Meta-Analyses
In health research, the Randomised Controlled Trial (RCT) is considered a high-quality study design. Participants are randomly assigned to receive either the treatment (collagen) or a placebo (an inactive substance), often without participants or researchers knowing who got what (double-blinding). This design helps minimize bias and determine if the collagen truly caused the observed effect.
Even more powerful evidence comes from Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. These studies meticulously gather data from multiple relevant RCTs on the same topic, assess their quality (including risk of bias, which we also explain in this article), and statistically combine (“pool”) the results. Think of it like a rigorous summary of all the best available studies, providing a more robust overall conclusion than any single trial alone.
A meta-analysis is a powerful type of research that statistically combines the results from multiple independent studies on the same topic, providing a stronger overall conclusion than any single study alone.
Evidence for Skin Health (Hydration, Elasticity, Wrinkles)
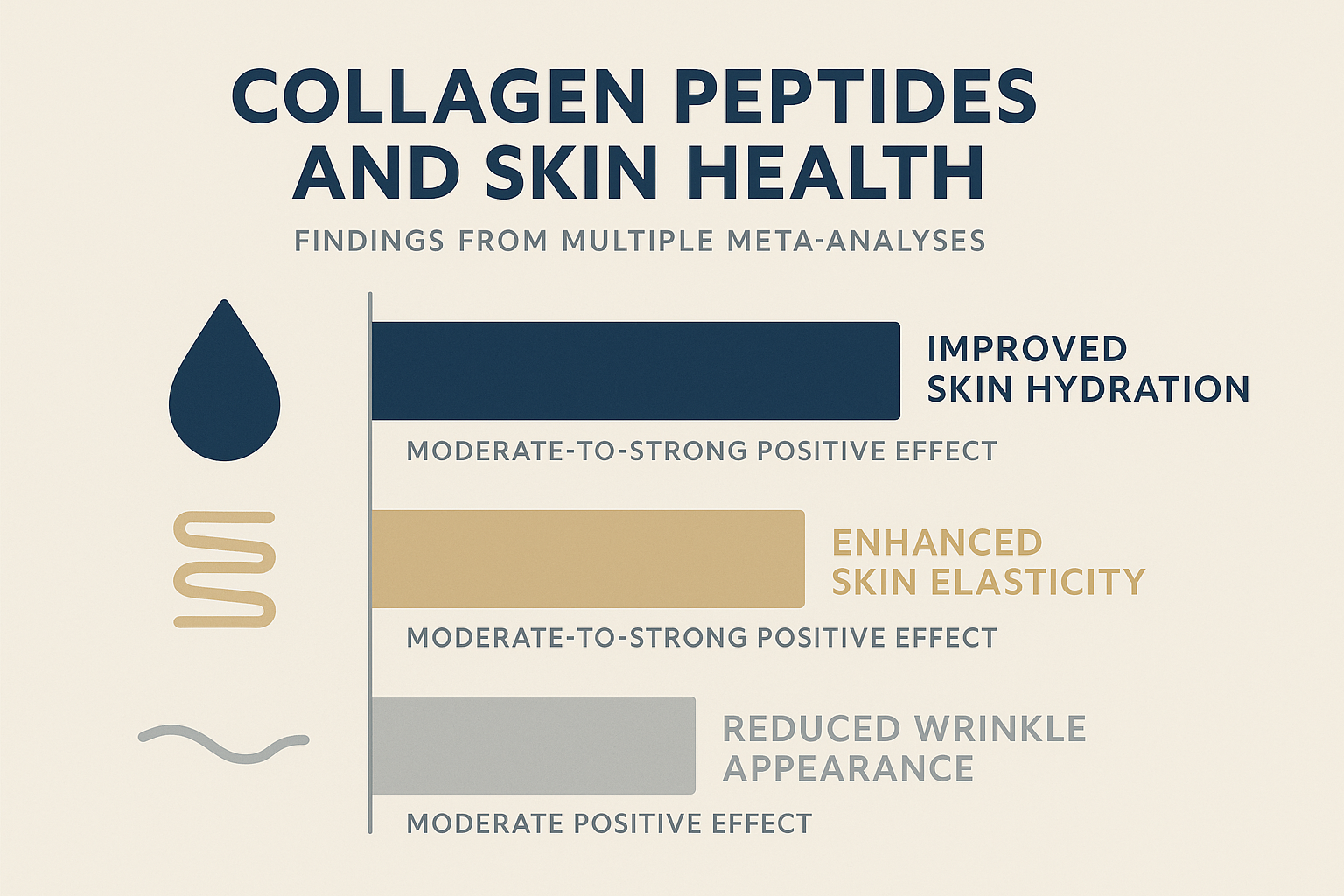
When considering A Meta-Analyses which assesed the results of many high-quality studies that quantified the effect of taking collagen supplements on the skin, a consistent picture emerges regarding collagen for skin before and after use. Recent reviews looking at numerous trials involving thousands of participants found that taking hydrolyzed collagen peptides regularly leads to noticeable, statistically significant improvements compared to taking a placebo:
- Improved Skin Hydration: The combined evidence shows collagen users experienced consistently better skin moisture levels than those taking a placebo (pooled SMD ≈ 0.63)
- Enhanced Skin Elasticity: Similarly, the pooled results indicate improvements in the skin’s ability to ‘snap back’ for the collagen groups compared to placebo (pooled SMD ≈ 0.72)
How do you translate SMD (Standardized Mean Difference) scores like ≈ 0.63 and ≈ 0.72?
SMD ≈ 0.2 indicates a Small effect size.
SMD ≈ 0.5 indicates a Medium or Moderate effect size.
SMD ≈ 0.8 indicates a Large effect size.
- The meta-analysis results suggest collagen peptides have a consistent moderate-to-strong positive effect on skin hydration and elasticity compared to placebo – a meaningful and noticeable difference for many.
- Reduced Wrinkle Appearance: Reviews also conclude that consistent intake (e.g., for 90 days) can effectively lead to a reduction in the appearance of wrinkles compared to placebo. You can access the Meta Analysis which is published on the PubMed platform.
Later in the blog we expalin research nuances and be able to understand potential biases.
Do Collagen Drinks & Powders Improve Skin?
Yes, the evidence supports this. Most successful clinical trials involve participants consuming hydrolyzed collagen peptides that have been dissolved in liquid – whether provided as a ready-made drink or a powder mixed into water or another beverage. This confirms that oral intake in liquid form is an effective delivery method for achieving the observed skin benefits. Products like collagen liquid, collagen powder, liquid collagen drink, or collagen sachets are common formats.
The effectiveness of liquid marine collagen or bovine collagen powder depends on the quality of the hydrolysis process and bioavailability of the peptides themselves once ingested. Read more about the hydrolysis process and assesing collagen quality in our “Marine vs Bovine Collagen”
Evidence for Joint Health
Collagen is a key component of cartilage. Some research, particularly on Osteoarthritis, suggests HC peptide supplementation may help improve joint function and reduce symptoms like pain/stiffness.
However, the evidence is more mixed than for skin health, and study quality varies. You can read more about best supplements for joints health in our dedicated article.
Evidence for Bone Health
Bone matrix is also rich in Type I collagen. Some studies, particularly in postmenopausal women, suggest potential BMD benefits with longer-term use (12+ months) of collagen peptides (~5g/day). Specific collagen peptides improve bone density in postmenopausal.
However, this is also an area requiring further investigation, especially across different populations.
Evidence for Other Areas (e.g., Gut Health, Muscle Mass)
While collagen provides amino acids like L-glutamine, which is known to be an important fuel source for intestinal cells, the specific effects of collagen peptides on the microbiome require more investigation.
Research on L-glutamine itself for gut support is more established. Emerging research is exploring whether some collagen peptides might influence the gut microbiome, potentially acting like a prebiotic, but more human studies are needed to confirm this effect.
Similarly, effects on muscle mass appear minimal without concurrent resistance training.
You can read more more about the Benefits of Hydrolysed Collagen here.
How Much Collagen to Take & How Long Until Results?
If you’re wondering how long do collagen supplements take to work, this section covers typical timelines.
Effective Dosages
For the skin benefits discussed, clinical studies typically use daily doses ranging from 2.5 grams to 10 grams of hydrolyzed collagen peptides, Meta Analysis 2023. Encouragingly, multiple studies show significant results at the lower end of this range, around 2.5g per day, Proksch 2014. There isn’t strong evidence that taking much higher doses provides significantly better skin results, suggesting a potential threshold effect
Timeline for Results
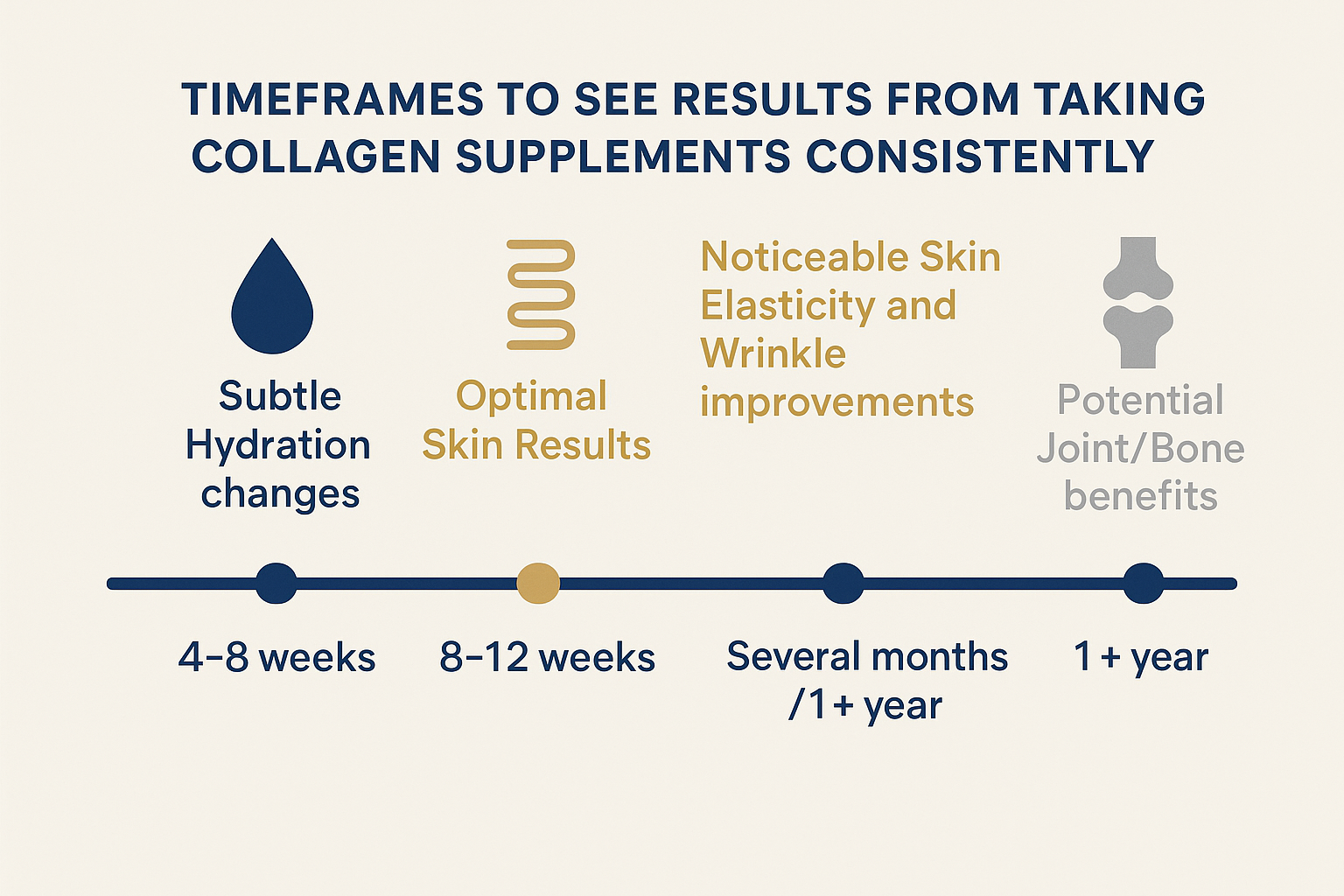
Patience and consistency are key when considering taking collagen before and after changes! Based on clinical trials, here is a general idea of how long for collagen to work, read more about How Long it Takes for Collagen to Work in our dedicated article.
- Noticeable Skin Improvements: Typically 8 to 12 weeks (for elasticity, wrinkles). This is often when people start seeing collagen before and after differences.
- Earlier Subtle Changes: Possibly 4 to 8 weeks (for hydration).
- Optimal Results: May take 3 to 6 months.
- Joints/Bones: Likely require longer timelines (several months / 1+ year).
Maintaining Results & Format Convenience
Consistency is crucial, as benefits are linked to daily intake and likely diminish if supplementation stops. Choosing a format that fits your routine, such as convenient single-serving collagen sachets, a liquid collagen drink, or mixing collagen powder. Remember when choosing the best supplement for you, assess molecular weight, formulation quality and dosage. These factor drive effectiveness not form. If you want to learn more about how to choose the best collagen supplement for you, read our dedicated guide.
Collagen Supplements: Limitations, Funding Bias & What to Consider
While the evidence is promising, a transparent discussion requires acknowledging important considerations and limitations surrounding collagen research and supplements. Understanding these helps set realistic expectations for taking collagen before and after results.
Understanding Research Nuances
While RCTs aim to be the gold standard for minimizing bias, it’s important to understand that limitations can still exist, affecting how we interpret results.
Industry Funding & Potential Bias
A significant point of awareness is that much of the published research on collagen supplements is funded or supported by the companies that manufacture or sell these products. This doesn’t automatically invalidate the results, but it does create a potential conflict of interest. There’s a risk of publication bias (where positive studies are more likely to get published than negative or inconclusive ones). Therefore, it’s crucial to look for findings supported by independent research groups and confirmed by systematic reviews and meta-analyses (which often assess the risk of bias in included studies, though specific funding breakdowns aren’t always reported in the final publication), similar to the Meta Anlaysis covered and linked in this article.

Other Study Limitations
Keep these common limitations in mind when evaluating collagen supplement research and setting expectations for collagen supplements before and after results:
- Small Sample Sizes & Short Durations: Many trials are relatively small and short-term (8-12 weeks typical), limiting statistical power and knowledge of long-term effects/safety. This is why observing noticeable collagen before and after changes may take longer than the study duration.
- Variability (Heterogeneity): Studies use different collagen types (e.g., bovine collagen, marine collagen), manufacturers, doses, measurement methods, and populations, making direct comparisons difficult.
Regulatory Context (UK)
In the UK and EU, collagen supplements are classified as food supplements, not medicinal products. They do not require pre-market approval for efficacy like medicines do. Quality control, purity, and actual peptide content can vary significantly between brands selling products like bovine collagen powder or marine collagen powder uk.
It’s essential to choose reputable brands that are transparent about their sourcing and processing and ideally provide evidence of third-party testing for quality and contaminants. When buying collagen look for this transparency.
COLLinstant® Quality Control, and Technical Specifications are accessible here.
Realistic Expectations (Magnitude of Effect)
It’s vital to have realistic expectations for collagen before and after results. Studies show moderate, not dramatic, changes. A 20% wrinkle reduction is measurable but won’t erase all lines. Collagen supplementation is one part of a holistic approach alongside lifestyle (SPF, diet).
The Verdict: Does Science Support Collagen Supplements?

So, back to our core question: does collagen really work?
Based on the current weight of scientific evidence, particularly from systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs, the answer is yes, oral hydrolyzed collagen peptides (whether from bovine/beef, or marine) can provide statistically significant, moderate improvements in key skin health markers (hydration, elasticity, wrinkles) for many individuals when used consistently at appropriate doses (e.g., 2.5g+/day for 8-12+ weeks).
The improvements are often seen when comparing collagen before and after use over this timeframe. Evidence for joints/bones is emerging but less consistent; other areas more preliminary.
However, this positive finding comes with crucial caveats. Results vary, benefits are moderate, long-term data is limited, potential for research bias exists, and product quality/formulation matters.
Ultimately, supporting your natural radiance involves informed, evidence-based choices. Critically evaluate claims, seek out information from reliable sources (especially meta-analyses), choose high-quality products from transparent brands (consider factors discussed in our Marive vs Bovine Collagen Guide, and look for quality in collagen powder or collagen liquid,, manage expectations, and view collagen supplementation as one potential component within your overall wellness strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Typically 8-12 weeks of consistent daily use are needed to see noticeable improvements in skin elasticity and wrinkles, although hydration might improve slightly sooner (~4 weeks). This addresses how long for collagen to work for skin. You can read more about the timeline and what to expect in our dedicated article here.
Based on studies typically lasting up to 12 weeks, hydrolyzed collagen peptides are generally considered safe for most healthy adults. Minor side effects like bloating can occasionally occur. Choosing reputable brands with purity testing for their collagen powder or liquid collagen drink products is advisable. Always look for brands that offer transparency when it comes to ingrediants and consult your doctor if you have health conditions or concerns.
For skin health, current evidence from meta-analyses suggests minimal significant difference in efficacy between high-quality hydrolyzed sources like bovine collagen and marine collagen. Processing (low MW peptides) is likely more critical for absorption than whether it's beef collagen or marine. Read more in our Marine vs Bovine Collagen Guide.
It's wise to be discerning. Look for findings supported by systematic reviews or meta-analyses. Be aware that some individual studies are funded by supplement manufacturers, which means results should be interpreted carefully. Focus on consistent findings across multiple studies and maintain realistic expectations about the moderate level of benefits typically observed when looking at collagen supplements before and after studies.
In the UK, you can find various forms including collagen powder, collagen liquid, collagen sachets uk, liquid marine collagen uk, marine collagen powder uk, and liquid collagen drink options, sourced from bovine collagen, marine, and occasionally beef collagen peptides. Look for hydrolysed bovine collagen or other hydrolysed sources for best absorption.
Join Us in Redefining Beauty
Subscribe for Exclusive Insights









