At Timeless Radiance, we understand the frustration of navigating the complex world of collagen supplements. With so many terms and claims, it’s hard to know what truly works. This article cuts through the confusion and explains the science of bioactive peptides in collagen – what they are, how they benefit you, and how to choose a high-quality supplement.
🧠 Prefer to watch instead of read?
Scroll to the end for our quick explainer 3.5 minutes video on Bioactive Peptides.
What Are Bioactive Peptides and How Do They Work?
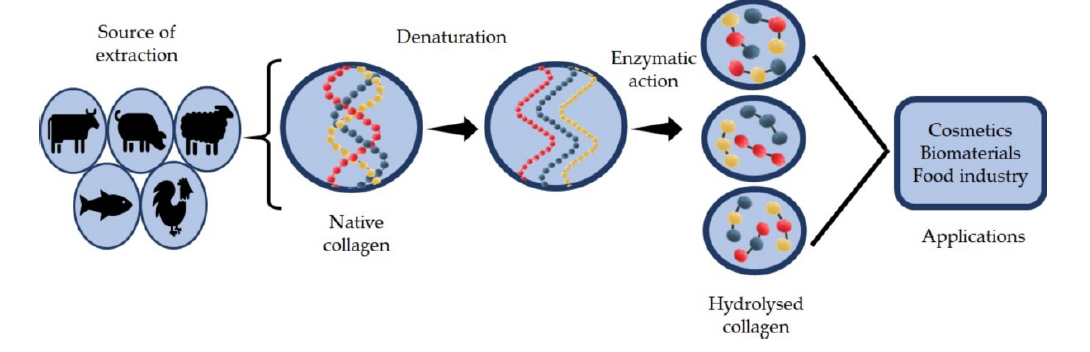
Bioactive peptides are short chains comprising specific sequences of amino acids, released when larger proteins are broken down, typically through enzymatic hydrolysis. Unlike the larger protein molecules they originate from, these peptides possess specific biological activities once absorbed by the body.
In the context of collagen, these peptides act as signalling molecules. They stimulate fibroblasts – the skin’s specialised cells responsible for collagen synthesis – encouraging them to increase the production of new collagen and other vital components of the extracellular matrix (like elastin and hyaluronic acid). This cellular stimulation contributes to improved skin firmness, hydration, and elasticity.
Sources and Extraction: The Science of Hydrolysed Collagen
Bioactive peptides are found in various protein sources, including dairy, fish, and collagen. In hydrolysed collagen supplements, an enzymatic process during production breaks down Type I and Type III collagen into low-molecular-weight peptides. Generally ranging from 0.3 to 8 kDa, with most bioactive peptides falling between 0.4 and 2 kDa, which can improve their bioavailability and absorption. While the hydrolysis method influences the composition of peptides, molecular weight ultimately determines their bioactivity and absorption.
The Proven Benefits of Bioactive Collagen Peptides
The excitement surrounding bioactive collagen peptides stems from their diverse, scientifically observed benefits that extend throughout the body. Research highlights their positive impact not only on skin appearance but also on cellular protection and reducing inflammation. Let’s explore some of the key advantages.
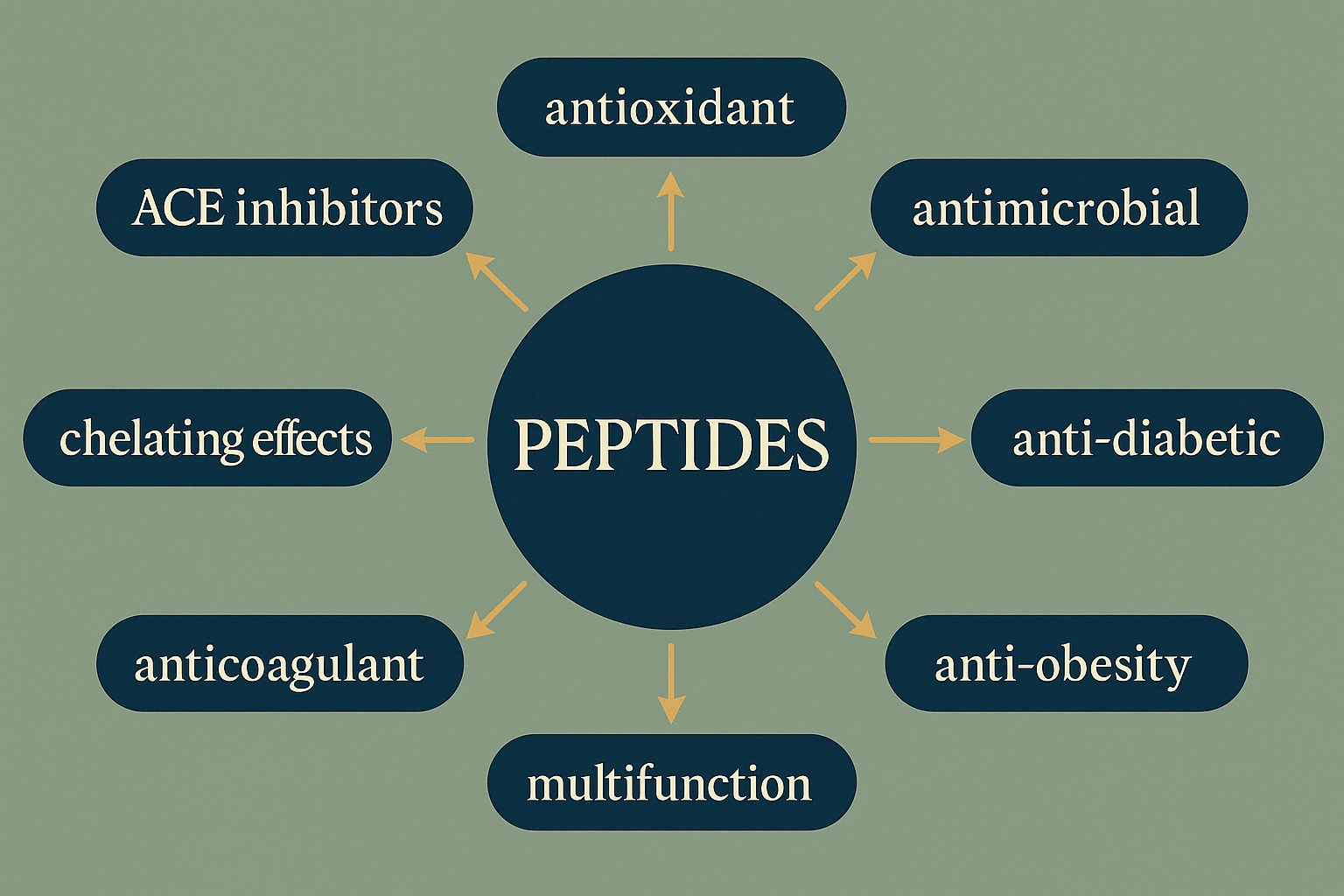
Stimulating Collagen Production for Youthful Skin
Fibroblasts are specialised skin cells responsible for producing collagen and the extracellular matrix (ECM) – the skin’s structural support network. Research, including a study published in the Frontiers in Nutrition, has shown that Prolyl-hydroxyproline (Pro-Hyp), a key collagen peptide found in the bloodstream after consuming hydrolysed collagen, supports the function of adult human dermal fibroblasts and boosts the synthesis of other vital ECM proteins like elastin, contributing to improved skin structure and resilience
Powerful Antioxidant Protection Against Free Radical Damage
Our skin is constantly exposed to factors generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), unstable molecules causing oxidative stress that damages cells and accelerates ageing. Certain collagen peptides, particularly those containing the amino acid hydroxyproline, have demonstrated potent antioxidant capabilities. They can effectively neutralise ROS, helping to protect skin cells from damage and reduce overall oxidative stress. This protective action slows down the degradation of existing collagen and supports long-term skin health. You can read more about this Research, published in the Frontier in Nutrition,
Reducing Inflammation for Improved Skin Health and Comfort
Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognised as a key driver of skin ageing and breakdown of tissues. Cytokines are signalling proteins that regulate inflammation; Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a notable pro-inflammatory cytokine. When unregulated, IL-6 contributes to inflammatory processes that degrade the skin matrix. You can learn more about teh role of inflammation in aging in Frontiers of Immunology. Specific collagen peptides, such as Hydroxyprolyl-Glycine (Hyp-Gly), have been shown to help downregulate IL-6 production. This reduction in inflammatory signalling supports better skin barrier function and overall skin health. You can read more about the research into the “Bioactivities, Applications, Saftey and Health Benefits of Bioactive peptides” in this study published on Frontiers of Nutrition.
Bioactive Peptides: Beyond Skin Deep - Joint, Bone, and Gut Health
While often discussed for their skin benefits, the positive effects of bioactive collagen peptides extend to other critical areas of health. Their unique properties support the integrity and function of joints, bones, and even the gut lining, contributing to overall well-being and resilience.
Supporting Joint Comfort and Mobility
Collagen is a primary component of cartilage, the tissue cushioning our joints. Specific collagen peptides, particularly dipeptides like Pro-Hyp, have been shown to reach joint tissues and stimulate chondrocytes (cartilage cells). Research indicates these peptides can enhance the synthesis of cartilage matrix components, potentially aiding repair processes and contributing to reduced joint discomfort and improved mobility, especially in individuals experiencing conditions like osteoarthritis. detailed research in to Bioactive Peptides role is published A Journal of Analytical Chemistry and Microbiology.
Promoting Bone Strength and Density
Collagen forms the flexible protein scaffold within our bones, providing essential structure and resilience alongside minerals. Ingested collagen peptides supply key amino acids like glycine and proline that are fundamental building blocks for this bone matrix. Furthermore, research suggests certain peptides may help stimulate osteoblasts, the specialised cells responsible for bone formation, potentially contributing to maintaining bone strength and density over time. A Journal of Analytical Chemistry and Microbiology

Nurturing a Healthy Gut Microbiome
Emerging research highlights the role of collagen peptides in supporting gut health. Peptides such as Pro-Hyp and Gly-Pro-Hyp appear to help maintain the integrity of tight junctions between cells in the gut lining. By supporting this intestinal barrier, they may reduce inflammation and permeability (“leaky gut”), promoting gut homeostasis.
Additionally, collagen peptides provide amino acids like glutamine, known to nourish intestinal cells. This contributes to a balanced gut environment. Further investigation is exploring the potential synergistic benefits of combining collagen peptides with prebiotics for optimal gut health support. Research into the role of L-glutamine in gut and overall health is published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
Choosing the Best Collagen Supplement: Understanding Peptide Profiles
Molecular Weight and Bioavailability: Why Size Matters
For collagen peptides to work, they need to be absorbed efficiently into the bloodstream. This is where bioavailability becomes crucial. Research consistently shows that hydrolysed collagen with a low molecular weight profile, ideally below 3kDa (kilodaltons), exhibits superior absorption compared to larger peptides or intact collagen molecules. These smaller peptides can more readily pass through the intestinal barrier and reach target tissues throughout the body. While the hydrolysis method influences the types of peptides present, the molecular weight is a primary determinant of overall bioavailability and subsequent bioactivity
The Role of Enzymatic Hydrolysis
The specific enzymes used during the hydrolysis process significantly influence the final composition and profile of the resulting bioactive peptides. Different enzymes cleave the collagen protein at different points, leading to variations in the types and ratios of peptides generated. Research comparing various hydrolysis methods confirms that enzyme selection is a critical factor affecting the final peptide profile and potentially its specific biological effects. Nutrients Journal.
Bovine vs. Marine Collagen: A Comparison of Peptide Profiles
When selecting collagen, both the source and the manufacturing process matter. Bovine collagen typically provides a blend of Type I & III collagen, offering broad support for skin, joints, and gut health. Marine collagen is primarily Type I.
While you might hear claims about one source having inherently ‘smaller’ or ‘more absorbable’ peptides, optimal absorption actually depends on effective enzymatic hydrolysis creating low molecular weight peptides (<3kDa) – a quality factor achievable in both well-processed bovine and marine collagen. The choice often comes down to the desired collagen types (I & III vs I) and ensuring quality processing.
For a thorough examination of bovine versus marine collagen, including a deeper look at absorption factors and which might suit your specific goals:
➡️ Read our dedicated comparison guide
Key Indicators of a High-Quality Collagen Supplement
Navigating supplement labels can be tricky. Here’s what to prioritise:
- Understanding Terminology: You might see “Bioactive Collagen Peptides® ” on some products. It’s vital to recognise this is often a trademarked brand name, not a unique scientific category. All properly hydrolysed collagen contains bioactive peptides, but the peptides profile may vary.
- Low Molecular Weight: Look for evidence of a low molecular weight profile, ideally specified as 3kDa or lower, for optimal absorption.
- Hydrolysed Type I & III Bovine Collagen: Choosing a supplement containing both major types from a bovine source offers more comprehensive support for skin, joints, bones, and gut health.
- High Concentration & Purity: While specific peptide concentrations are rarely listed, look for products with minimal fillers, unnecessary additives, or bleach.
- Reputable Sourcing & Transparency: Choose brands that are transparent about their sourcing, manufacturing processes, and quality control testing (e.g., third-party certifications). You can learn more about our supplier COLLinstant® and their manufacturing process here.
- Clinically Backed Ingredients (If available): Some brands may use specific peptide compositions tested in clinical studies; if so, they should provide evidence.
How to Use Collagen Peptides for Optimal Results
Incorporating collagen peptides into your routine is simple, but consistency and appropriate dosage are key to experiencing the benefits. Here’s what the research suggests regarding intake and the typical timeframe for observing results.
Recommended Daily Intake and Timeframe for Visible Benefits
Based on clinical studies, recommended daily dosages often range from 2.5 to 10 grams for noticeable skin health benefits (like hydration and elasticity) and potentially 10 to 15 grams for joint support.
Consistency is crucial. You can learn more about How Long it Takes for Collagen Supplements to work in our dedicated article.

Empower Your Radiance with Bioactive Peptides
Bioactive peptides derived from high-quality, hydrolysed bovine collagen offer a scientifically supported avenue to nurture your health from within. Their demonstrated benefits for skin vitality, joint function, gut health, and potentially bone strength make them a valuable addition to a holistic wellness strategy. By understanding the importance of factors like peptide diversity, low molecular weight for bioavailability, and the comprehensive nature of the Types of collagen, you can make informed choices. Selecting a premium supplement empowers you to support your body’s resilience and embrace graceful ageing.
Stay healthy , Stay radiant
FAQs
Yes, the benefits of bioactive collagen peptides extend beyond the skin. For joints, specific peptides can stimulate cartilage cells (chondrocytes) and support the production of cartilage matrix, potentially aiding in joint comfort and mobility. In bones, they provide essential amino acids for the bone matrix and may stimulate bone-forming cells (osteoblasts). For gut health, certain peptides can help maintain the integrity of the gut lining, potentially reducing inflammation and supporting a healthy gut environment.
Generally, collagen peptide supplements are considered safe for most healthy individuals with few reported side effects. Some people may experience mild digestive issues like bloating, gas, or a feeling of fullness, especially when starting a new supplement. It's always recommended to start with a lower dose and gradually increase to the recommended amount. If you have any pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications, it's best to consult with your healthcare provider before 1 starting any new supplement.
When selecting a collagen supplement, prioritize products that specify a low molecular weight (ideally below 3kDa) for optimal absorption. Look for "hydrolysed collagen," preferably Type I & III from a bovine source for comprehensive benefits. Choose supplements with minimal fillers or additives and opt for brands that are transparent about their sourcing and manufacturing processes, potentially looking for third-party certifications.
No, they are not exactly the same. Hydrolysed collagen is the form of collagen that has been broken down into smaller peptides through enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioactive collagen peptides are these smaller fragments that possess specific biological activities once absorbed. So, hydrolysation is the process that yields bioactive peptides.
Both bovine (typically Type I & III) and marine (primarily Type I) collagen can be effectively hydrolysed to produce bioactive peptides with good absorption, provided the molecular weight is low (below 3kDa). The main difference lies in the types of collagen they primarily contain. Bovine offers a broader range for skin, joints, and gut, while marine is mainly Type I, which is also beneficial for skin and bones. The quality of the hydrolysis process is more critical for absorption than the source itself.
Molecular weight refers to the size of the collagen peptides, measured in kilodaltons (kDa). Low molecular weight, ideally below 3kDa, signifies that the peptides are small enough to be efficiently absorbed through the intestinal barrier into the bloodstream. Better absorption leads to greater bioavailability, allowing the bioactive peptides to reach their target tissues and exert their beneficial effects more effectively.
Join Us in Redefining Beauty
Subscribe for Exclusive Insights









